Dead Letter Queue (DLQ)
The Dead Letter Queue is where webhook events go after failing all automatic retry attempts. Learn how to review, debug, and manually retry failed events.
What is the Dead Letter Queue?
When a webhook fails to be delivered to your destination after 5 automatic retry attempts (over approximately 13 minutes), it's moved to the Dead Letter Queue.
The DLQ ensures you never lose a webhook event - even when your application is down for extended periods.
When Events Move to DLQ
Events move to the DLQ when:
- ❌ Your destination returns 5xx errors consistently
- ❌ Your destination times out (30 seconds)
- ❌ Your destination is unreachable (DNS failure, connection refused)
- ❌ SSL/TLS certificate errors
- ✅ All 5 automatic retries have been exhausted
- 1st attempt: Immediate
- 2nd attempt: After 5 seconds
- 3rd attempt: After 25 seconds
- 4th attempt: After 125 seconds (~2 minutes)
- 5th attempt: After 625 seconds (~10 minutes)
- Then → Moves to DLQ
Accessing the Dead Letter Queue
- Log in to your dashboard
- Click the "Dead Letter Queue" tab
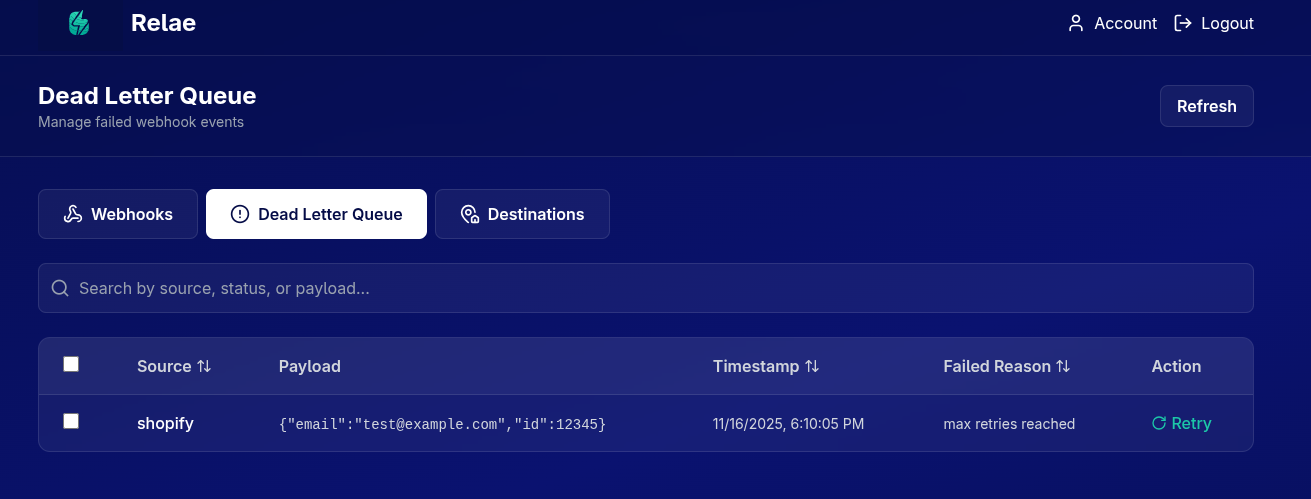
Understanding the DLQ Table
Each failed event shows:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Checkbox | Select events for bulk retry |
| Source | The vendor that sent the webhook |
| Payload | Preview of the webhook data |
| Timestamp | When it was originally received |
| Failed Reason | Why delivery failed |
| Retry Button | Manually retry this specific event |
Failed Reasons Explained
Connection Refused
Your destination server refused the connection
Common causes:
- Application is down
- Wrong destination URL
- Firewall blocking Relae's IPs
Fix:
- Verify your destination URL is correct
- Ensure your application is running
- Check firewall rules
Timeout
Request timed out after 30 seconds
Common causes:
- Slow database queries in your webhook handler
- Processing too much data synchronously
- Network latency issues
Fix:
- Optimize your webhook handler performance
- Process webhooks asynchronously (return 200 immediately)
- Add database indexes
500 Internal Server Error
Your application returned HTTP 500
Common causes:
- Unhandled exception in your code
- Database connection issues
- Missing required data
Fix:
- Check your application error logs
- Add error handling to webhook endpoint
- Validate required fields exist
Invalid SSL Certificate
SSL certificate verification failed
Common causes:
- Expired SSL certificate
- Self-signed certificate
- Certificate chain issues
Fix:
- Renew your SSL certificate
- Use a valid CA-signed certificate
- Ensure certificate chain is complete
DNS Failure
Could not resolve hostname
Common causes:
- Domain doesn't exist
- DNS not propagated yet
- DNS server issues
Fix:
- Verify domain is correct
- Wait for DNS propagation (up to 48 hours)
- Test with curl to confirm DNS works
Viewing Event Details
Click on any event row to see:
Full Payload
The complete JSON body of the webhook:
{
"id": "evt_1234567890",
"type": "payment_intent.succeeded",
"data": {
"object": {
"id": "pi_1234567890",
"amount": 5000
}
}
}
Original Headers
All headers sent by the vendor:
{
"content-type": "application/json",
"x-stripe-signature": "t=1701234567,v1=abc123...",
"user-agent": "Stripe/1.0"
}
Retry History
See all retry attempts with timestamps and error messages.
Retrying Events
Single Event Retry
- Click the "Retry" button on the event row
- Confirm the retry in the modal
- Event is immediately reprocessed
If successful:
- ✅ Event moves from DLQ to Webhooks tab
- ✅ Status changes to "delivered"
If still failing:
- ❌ Event stays in DLQ
- ❌ New failure reason is shown
Bulk Retry
Retry multiple events at once:
- Check the boxes for events to retry
- Click "Retry (X)" button in the header
- Confirm bulk retry
- All selected events are reprocessed
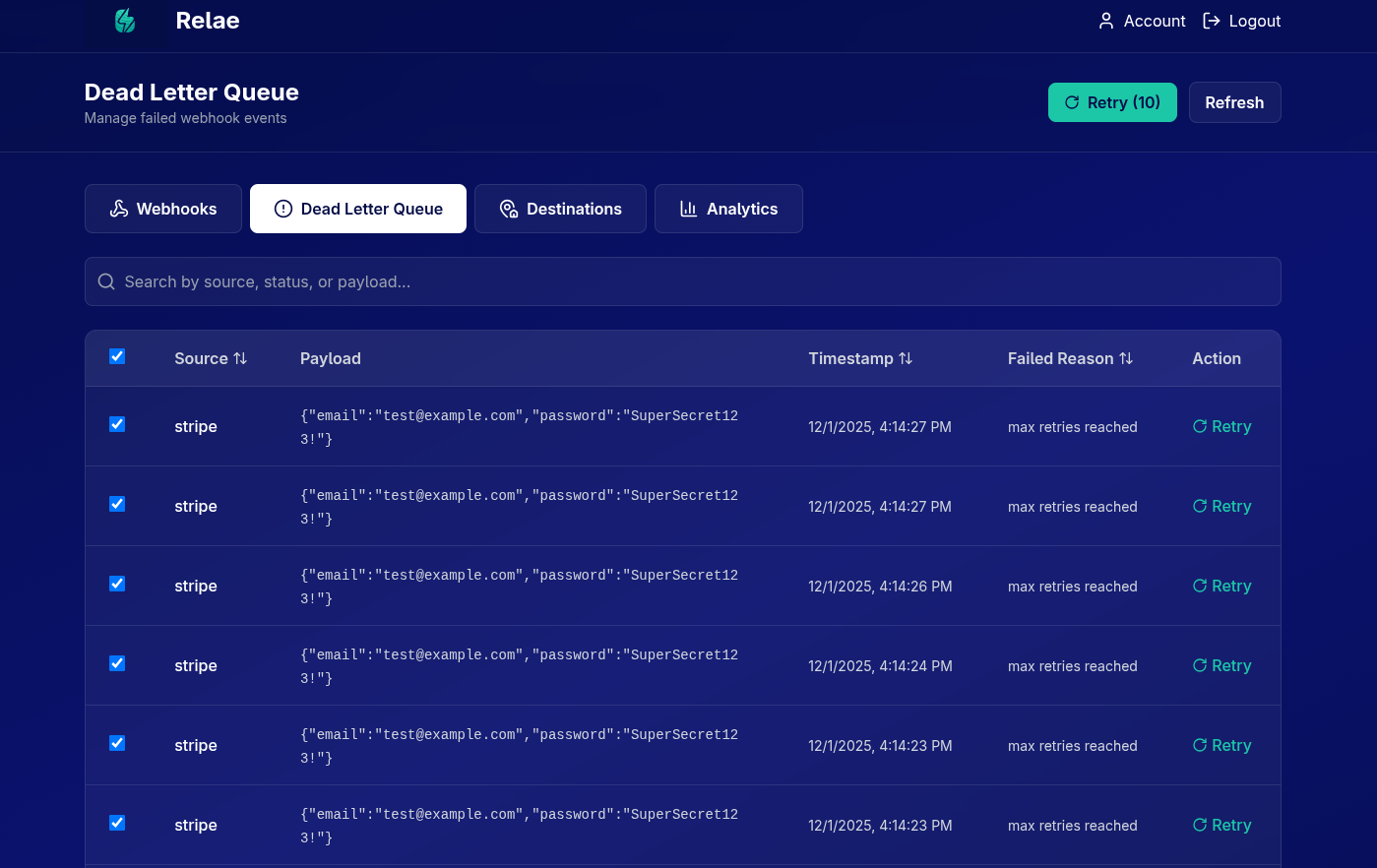
Bulk retry is useful after fixing an issue that affected multiple events (e.g., after a deployment or server restart).
Searching & Filtering in DLQ
Use the search bar to find specific failed events:
Examples:
stripe- Find all Stripe failurestimeout- Find all timeout errorspayment_intent- Find specific event types500- Find all 500 errors
Best Practices
1. Monitor DLQ Daily
Check your DLQ regularly for:
- Unexpected failures
- Patterns in error messages
- Events that need attention
2. Fix Root Causes
Don't just retry - fix the underlying issue:
3. Process Asynchronously
To avoid timeouts, acknowledge webhooks immediately:
// ✅ Good: Quick acknowledgment
app.post("/webhooks", async (req, res) => {
// Return 200 immediately
res.status(200).send("OK");
// Process asynchronously
processWebhookAsync(req.body);
});
// ❌ Bad: Slow synchronous processing
app.post("/webhooks", async (req, res) => {
await slowDatabaseQuery();
await sendEmail();
await updateCache();
res.status(200).send("OK"); // Too late!
});
4. Add Idempotency
Handle duplicate retries gracefully:
app.post("/webhooks", async (req, res) => {
const eventId = req.body.id;
// Check if already processed
const exists = await db.findEvent(eventId);
if (exists) {
return res.status(200).send("Already processed");
}
// Process new event
await processWebhook(req.body);
await db.saveEvent(eventId);
res.status(200).send("OK");
});
Understanding Retry Behavior
What Gets Retried
When you retry an event from the DLQ:
- ✅ Same payload
- ✅ Same headers (except timestamps)
- ✅ Fresh HMAC signature
- ✅ New timestamp in
X-Relae-Timestamp
What Changes
- 🔄 New attempt timestamp
- 🔄 Fresh signature (verify with current token)
- 🔄 Updated retry count in metadata
Common Scenarios
Scenario 1: Deployment Downtime
Situation: You deployed new code and your app was down for 20 minutes. 100 events in DLQ.
Solution:
- Verify deployment is successful
- Test with curl:
curl -X POST your-destination-url - Select all events in DLQ
- Bulk retry
- Monitor for successful delivery
Scenario 2: Database Connection Issues
Situation: Database was down, webhooks returning 500 errors.
Solution:
- Fix database connection
- Add connection retry logic to app
- Test webhook endpoint works
- Retry failed events from DLQ
Scenario 3: Wrong Destination URL
Situation: Typo in destination URL, all webhooks failing with "Connection Refused".
Solution:
- Go to Destinations tab
- Edit the destination
- Fix the URL typo
- Save changes
- Return to DLQ and bulk retry
Scenario 4: Timeout During High Load
Situation: Heavy traffic caused timeouts, some webhooks in DLQ.
Solution:
- Optimize webhook handler (process async)
- Scale application servers
- Add caching layer
- Retry timed-out events from DLQ
Debugging Failed Events
Step-by-Step Debugging
-
Click on failed event to view details
-
Check the failed reason
- Connection issue? Check destination URL
- Timeout? Optimize your handler
- 500 error? Check application logs
-
Test destination URL
curl -X POST https://your-destination-url.com/webhook \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"test": true}' -
Review application logs
- Check around the timestamp
- Look for exceptions or errors
- Verify webhook was received
-
Verify signature verification
- Make sure you're using correct endpoint token
- Check signature format:
sha256={hash} - Validate timestamp tolerance
-
Fix the issue in your application
-
Retry the event from DLQ
Using Event Details for Debugging
The event details modal shows everything you need:
{
"headers": {
"x-relae-signature": "sha256=abc123...",
"x-relae-timestamp": "1701234567",
"x-relae-source": "stripe",
"content-type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
// Full webhook payload
},
"metadata": {
"retry_count": 5,
"failed_reason": "Connection refused",
"last_retry_at": "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z"
}
}
Data Retention in DLQ
Events in the DLQ follow your tier's retention policy:
| Tier | DLQ Retention |
|---|---|
| Builder | 7 days |
| Launch | 14 days |
| Scale | 30 days |
| Enterprise | Custom |
Failed events are automatically deleted after the retention period. If you need to keep them:
- Export the payload (copy/paste)
- Store in your own systems
- Or upgrade to a tier with longer retention
Preventing DLQ Events
The best strategy is to prevent events from reaching the DLQ:
1. Reliable Infrastructure
- Use load balancers
- Auto-scaling groups
- Health checks
2. Fast Webhook Handlers
- Return 200 immediately
- Process asynchronously
- Keep handlers under 5 seconds
3. Error Handling
app.post("/webhooks", async (req, res) => {
try {
// Acknowledge immediately
res.status(200).send("OK");
// Process with error handling
await processWebhook(req.body);
} catch (error) {
// Log but don't throw
console.error("Webhook processing error:", error);
// Event still acknowledged successfully
}
});
4. Monitoring
- Set up uptime monitoring
- Track response times
- Alert on elevated error rates
5. Testing
- Test webhook endpoints regularly
- Simulate failures in staging
- Verify retry behavior
Next Steps
Need Help?
Having trouble with the DLQ?
- 📧 Email: support@relaehook.com
- 💬 Check the FAQ
- 🐛 Report issues on GitHub